It is very important for an individual to determine the residential status as the taxability under Income Tax Act 1961 is depends on the residential status of individuals. There are three types of residential status of individuals which are as follows-
1. Resident
2. Resident but not Ordinary Resident (RNOR)
3. Non–Resident (NR)
Taxability of Income of Persons with different status are as under-
Scope of Income | Resident | RNOR | NR |
1. Income received or deemed to be received In India during the year | Yes | Yes | Yes |
2. Income accruing or arising or deemed to accrue or arise in India during the year | Yes | Yes | Yes |
3. Income accruing or arising outside India during the year from a business controlled in or a profession set up in India. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
4. Income accruing/arising in India from a business/profession controlled/ set up Outside India. | Yes | Yes | No, in case no income related to Indian Operation |
5. Income accruing/arising outside India during a year from a foreign source | Yes | No | No |
6. Income which accrues or arises outside India and received outside India during the years preceding the previous year and remitted to India during the previous year. | Yes | No | No |
In order to determine the residential status of an Individual, one is required to check the residency rule as explained in section 6 of Indian Income Tax Act.
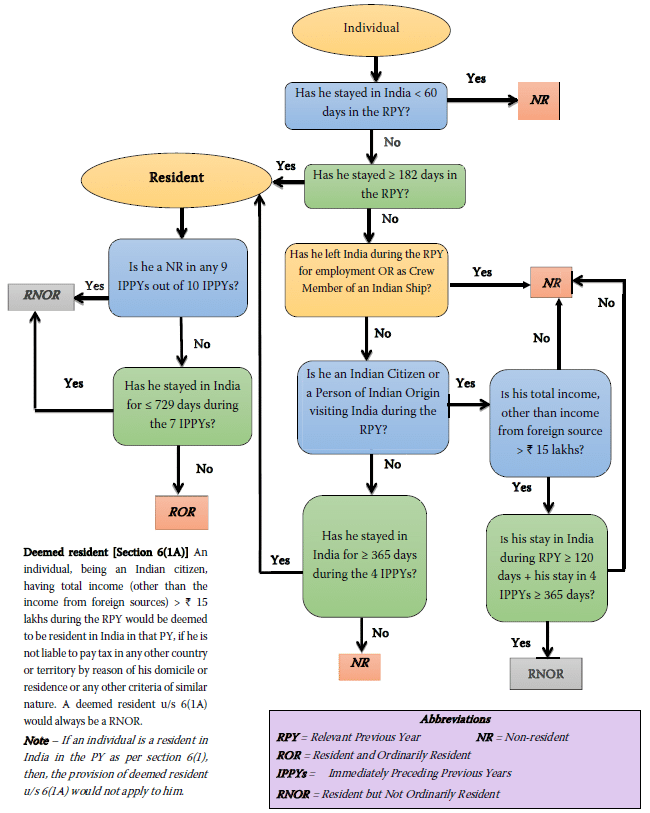
*Source- ICAI Saransh, Direct Tax Laws & International Taxation
Read more Articles :


0 Comments